这篇文章主要介绍一下vue-router插件的完成原理。
vue路由的作业流程
首要了解一下vue路由的作业流程,路由分为后端路由和前端路由。
后端路由
- 在地址栏中输入url
- 该恳求会被直接发送到服务器
- 服务器解析恳求中的途径并返回对应的页面
缺陷:发送恳求次数过多会对后台服务器造成比较大的压力,所以就出现了前端路由。
前端路由
- 在地址栏中输入url
- 该地址会被js进行解析
- 找到对应的页面后进行烘托
路由形式
前端路由的两种形式:Hash和History
hash形式
- #号后边的便是hash值的内容
- 能够经过
location.hash获取地址栏中的hash值 - 能够经过
window.onhashchange监听hash值的改动
history形式
- 地址栏/后即为正常的途径
- 能够经过
location.pathname获取地址栏中的途径 - 能够经过
window.onpopstate监听路由值的改动
vue路由的作业原理
graph TD
url改动 --> 触发监听事情 --> 改动vue-router中的currentRoute变量 --> vue监听currentRoute变量 --> 获取到对应的组件 -->render新组件
手写vue-router
列一下咱们一共需求了解的常识点:
- vue.use()注册插件机制
- vueRouter结构函数
- 两个大局组件:router-link和router-view
- main.js中为什么需求注入vueRouter的实例
vue.use()
vue.use办法在注册插件机制时运用的,它承受两个参数,第一个参数是插件自身,第二个参数是要传递给插件的选项。插件自身能够是一个函数也能够是一个目标,当是一个函数时use办法会当即履行该办法:
// 能够在main.js文件中进行测试
function a(){
console.log(100)
}
Vue.use(a) // 100
假如是一个目标的话则目标自身必须有一个install的办法,然后use会直接履行传入目标中的install办法,并且install办法中的第一个参数为vue的结构函数,有了vue的结构函数咱们就能够在里面运用vue相关的一些api:
let obj = {
install:function(vue){
console.log(120)
console.log(vue)
}
}
Vue.use(obj) // 120 function Vue(options) {...}
// 或者是
function a(){
console.log(100)
}
a.install = function(120){
console.log(120)
}
Vue.use(a) // 120
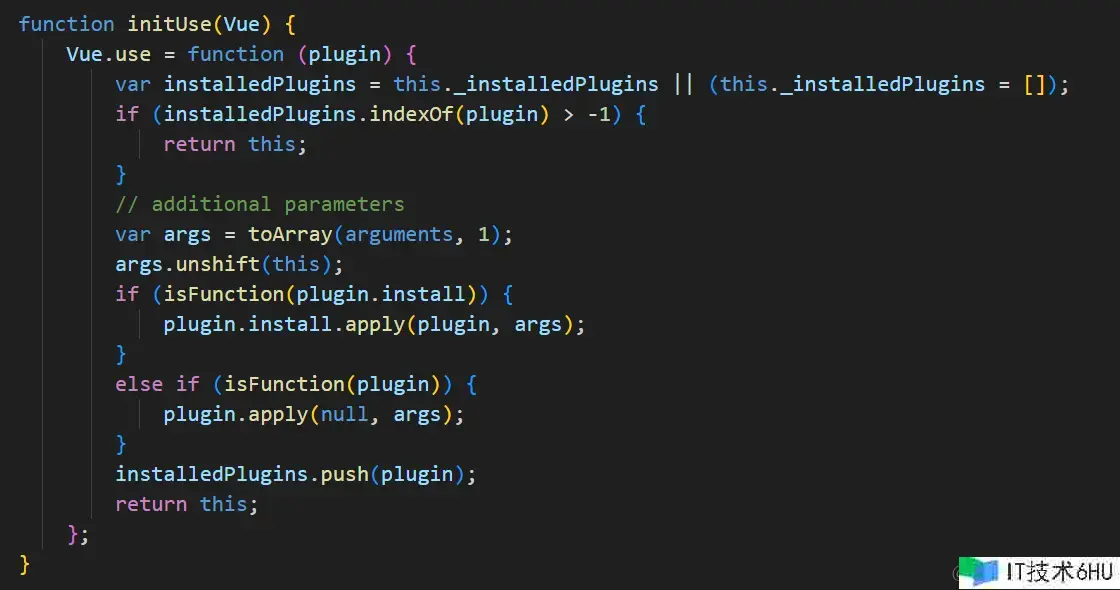
最终假如对同一个插件进行重复注册,那么该插件只会被装置一次,下面来看一下这块儿的源码:
能够直接在node_modules中查找vue要害字,然后找到dist文件夹下的vue.js文件。
能够看到前三行代码便是用来避免重复注册插件,然后往下能够看到把this直接放在了参数列表中的第一位也便是install办法的第一个参数,再往下便是判别插件自身是否有install特点并且是一个办法并进行履行。
vueRouter结构函数
在router.js中咱们能够看到:
const router = new VueRouter({});
阐明Vuerouter是一个结构函数,下面咱们来自己完成一个VueRouter的结构函数。
首要新建一个myRouter的文件夹以及它下面的index.js文件并进行途径的修正:
在index.js文件中咱们运用类来完成:
class VueRouter {
constructor() {
}
}
// 增加install办法
VueRouter.install = function (_vue) {
}
export default VueRouter;
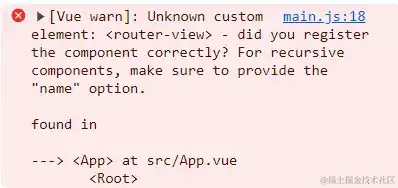
这时页面提示有报错:
也便是缺少了router-link和router-view两个大局组件,下面来完成一下。
完成router-link标签
持续在之前的代码中进行扩展:
let Vue;
class VueRouter {
constructor() {
}
}
// 增加install办法
VueRouter.install = function (_vue) {
Vue = _vue;
// 创立两个大局组件
Vue.component('router-link', {
// 运用render函数创立 router-link相当于a标签
render(h) {
return h('a', 'router-link')
}
})
Vue.component('router-view', {
// 运用render函数创立 router-view相当于占位符
render(h) {
return h('div', 'router-view')
}
})
}
export default VueRouter;
先运用Vue.component办法创立两个大局组件,这样就不会再有报错信息了。
router-link作为一个a标签应该具有超链接的特点,所以咱们能够运用h函数的第二个参数为其设置特点(不了解h函数的我就没办法喽 h函数)
// 以下为要害代码,其余的同上面保持一致
Vue.component('router-link', {
render(h) {
return h('a', {
attrs: { href: '#' }
}, 'router-link')
}
})
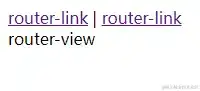
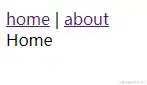
如图所示:
解决完这个问题后接下来便是跳转的问题了,在vue中router-link的跳转是经过给组件传递一个to特点来完成跳转:
<router-link to="/">home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">about</router-link>
那咱们能够在自己创立的大局组件中获取到该特点并完成地址栏路由的改动:
Vue.component('router-link', {
// 在当时组件中运用props承受传递的值
props:{
to:{
required:true,
type:String,
}
},
render(h) {
return h('a', {
// this指向的是当时router-link组件的实例
attrs: { href: '#'+this.to }
}, 'router-link')
}
})
这时点击就能够在地址栏中看到地址栏路由的改动。
那如安在页面中显示咱们自界说的名称呢?
那自然而然应该想到插槽的概念了。
Vue.component('router-link', {
props: {
to: {
required: true,
type: String,
}
},
render(h) {
return h('a', {
attrs: { href: '#' + this.to }
}, this.$slots.default) // 运用默许插槽
}
})
router-link标签到这儿就结束了,下面再来完成router-view标签。
完成router-view标签
完成router-view主要是经过监听路由的改动,运用当时的路由获取到对应的组件并进行烘托。
class VueRouter {
constructor(options) {
// 当时的路由
this.currentRoute = '';
// 用户界说的路由规矩
this.routes = options.routes;
// 路由形式
this.mode = options.mode || 'hash';
// 监听路由改动
this.init()
}
init() {
if (this.mode == 'hash') {
window.addEventListener("hashchange", () => {
this.currentRoute = location.hash.slice(1); // 去除前面的#号与用户装备的路由规矩表里保持一致
console.log(this.currentRoute);
})
}
}
}
这时分已经完成了路由的监听,在页面中切换会发现地址栏路由会发生改动并且能够获取到当时的路由值,接下来便是根据当时路由获取对应的组件。
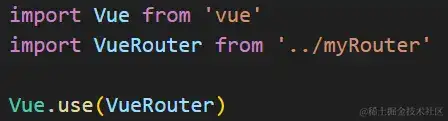
那么现在的问题便是如安在router-view大局组件中获取路由信息,这时分咱们能够运用Vue.mixin办法进行大局混入,经过大局混入的办法能够在里面给每个组件设置路由的相关信息。在Vue中咱们会在main.js文件中把router实例传递给Vue结构函数:
new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
经过this.$options能够获取vue中一切实例组件的信息
VueRouter.install = function (_vue) {
Vue = _vue;
Vue.mixin({
// 在每个组件的beforeCreate钩子函数中设置
beforeCreate() {
console.log(this.$options.name)
}
})
Vue.component('router-view', {
render(h) {
return('div','router-view');
}
})
}
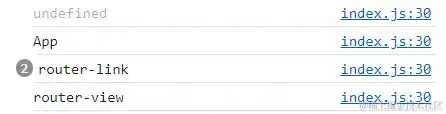
打印结果自上而下分别为main.js文件、App.vue、router-link、router-view组件,由于咱们能够获取到main.js文件中的装备项,所以也就能获取到用户装备的路由信息,之后再经过mixin办法同享给其他一切的组件,这便是为什么需求在main.js文件中注入vueRouter的实例
VueRouter.install = function (_vue) {
Vue = _vue;
Vue.mixin({
// 在每个组件的beforeCreate钩子函数中设置
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options.router) { // 判别是否是根实例
Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router // 让每个组件实例都能够拜访路由信息
}
}
})
Vue.component('router-view', {
render(h) {
const currentRoute = this.$router.currentRoute;
const routes = this.$router.routes;
// 获取到当时的路由信息与一切的路由信息进行匹配
const obj = routes.find(item => {
return item.path == currentRoute
});
return h(obj.component)
}
})
}
这时分组件已经烘托成功了,可是切换的时分组件并没有更新,这是由于currentRoute这个变量不是呼应式的,所以咱们需求把它变为呼应式数据,能够直接运用Vue中提供的api:
let Vue;
class VueRouter {
constructor(options) {
// this.currentRoute = '/';
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, 'currentRoute', '/') // 运用defineReactive办法界说currentRoute变量
// 用户界说的路由规矩
this.routes = options.routes;
// 路由形式
this.mode = options.mode || 'hash';
// 监听路由改动
this.init()
}
}
完好代码
let Vue;
class VueRouter {
constructor(options) {
// 当时的路由
// this.currentRoute = '/';
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, 'currentRoute', '/')
// 用户界说的路由规矩
this.routes = options.routes;
// 路由形式
this.mode = options.mode || 'hash';
// 监听路由改动
this.init()
}
init() {
if (this.mode == 'hash') {
window.addEventListener("hashchange", () => {
this.currentRoute = location.hash.slice(1); // 去除前面的#号与用户装备的路由规矩表里保持一致
})
}
}
}
VueRouter.install = function (_vue) {
Vue = _vue;
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options.router) {
Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router
}
}
})
Vue.component('router-link', {
props: {
to: {
required: true,
type: String,
}
},
render(h) {
return h('a', {
attrs: { href: '#' + this.to }
}, this.$slots.default)
}
})
Vue.component('router-view', {
render(h) {
const currentRoute = this.$router.currentRoute;
const routes = this.$router.routes;
const obj = routes.find(item => {
return item.path == currentRoute
});
return h(obj.component)
}
})
}
export default VueRouter;
上述代码仅仅讲解了以下vue-router比较中心的一些东西,想了解更多的常识能够检查vue-router的源码。