概述
本文首先以 FFmpeg 视频解码为主题,主要介绍了 FFmpeg 进行解码视频时的主要流程、基本原理;其次,文章还讲述了与 FFmpeg 视频解码有关的简单应用,包括如何在原有的 FFmpeg 视频解码的基础上按照一定时间轴顺序播放视频、如何在播放视频时加入 seek 的逻辑;除此之外,文章重点介绍了解码视频时可能容易遗漏的细节,最后是简单地阐述了下如何封装一个具有基本的视频解码功能的 VideoDecoder。
前言
FFmpeg
FFmpeg 是一套可以用来录制、转换数字音频、视频,并能将其转化查找算法有哪些为流的开源计算机程序,它可生成用于处理和操作多媒体数html文件怎么打开据的库,其中包含了先进的音视频解码库libavcodec和音视线程和进程的区别是什么频格式转换库libavformat。
FFmpeg 六大常用功能html模块
- libavfo线程数越多越好吗rmat:多媒体文件或协议的封线程安全装和解封装库,如 mp4、flv 等文件封装格式,rtmp、rtsp 等接口卡网络协议封装格式;
- libavcod线程撕裂者ec:音视频解码核心库;
- libavfilter:音视频、字幕滤镜库;
- libswscale:图像空间数据类型格式转换库;
- libswresample:音频重采样库;
- libavutil:工具库
视频解码基础入门
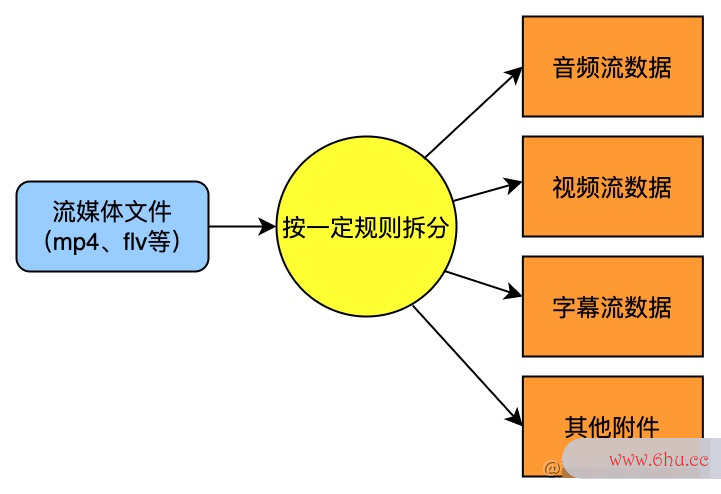
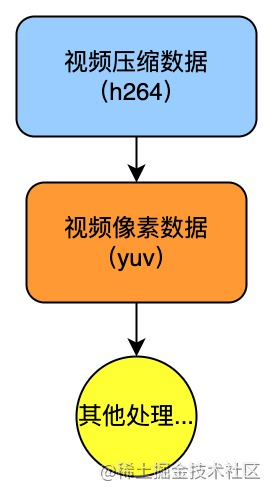
- 解复用(Demux):解复用也可叫解封装。这里有一个概念叫封装格式,封装格式指的是音视频的组线程合格式,常见的有 mp4、flv、mkv 等线程安全。通俗来讲,封装是将音频流、视频流、字幕流以及其他附件按一定规则组合线程成一个封装的产物。而解封装起着与封装相反的作用,将一个流媒体文件拆线程撕裂者解成音频数据空间数据类型有哪些和视频数据等。此时拆分后数据是经过压缩编码的,常见的视频压缩数据格式有 h264。
- 解码(Decode):简单来说,就是对压缩的编码数据解压成原始的视频像素数据,常用的原始视频像素数据格式有 yuv。
- 色彩空间转换(Color Space Convert):通常对于图像显示器来说,它是通过 RGB 模型来显示图像的,但在传输图像数据时使用 YUV 模型可以节省带宽。因此在显示图像时就需要将 yuv 像素格式接口类型的数据转换成 rgb 的像素格式后再进行渲染。
- 渲染(Ren线程的几种状态der):将前面已经解码和进行色彩空间转换的每一个视频帧的数据发送给显卡以查找算法绘制在屏幕画面上。
一、 引入 FFmpeg 前的准备工作
1.1 FFmpeg so 库编译
- 在线程池的七个参数 FFmpeg 官网下载源码库并解压;接口测试
- 下载 NDK 库并解压;
- 配置解压后的 FFmpeg 源码库目录中的 con接口测试figure,修改高亮部分几个参数为以下的内容,主要目的是生成 Android 可使用的 名称-版本.so 文件的格式;
#
#buildsettings
SHFLAGS='-shared-Wl,-soname,$$(@F)'
LIBPREF="lib"
LIBSUF=".a"
FULLNAME='$(NAME)$(BUILDSUF)'
LIBNAME='$(LIBPREF)$(FULLNAME)$(LIBSUF)'
SLIBPREF="lib"
SLIBSUF=".so"
SLIBNAME='$(SLIBPREF)$(FULLNAME)$(SLIBSUF)'
SLIBNAME_WITH_VERSION='$(SLIBNAME).$(LIBVERSION)'
#已修改配置
SLIBNAME_WITH_MAJOR='$(SLIBNAME)$(FULLNAME)-$(LIBMAJOR)$(SLIBSUF)'
LIB_INSTALL_EXTRA_CMD='$$(RANLIB)"$(LIBDIR)/$(LIBNAME)"'
SLIB_INSTALL_NAME='$(SLIBNAME_WITH_MAJOR)'
SLIB_INSTALL_LINKS='$(SLIBNAME)'
#
- 在 FFmpeg 源码库目录下新建脚本文件
build_android_a接口文档rm_v8a.sh,在文件中配置 NDK 的路径,并输入下面其他的内容;
#清空上次的编译
makeclean
#这里先配置你的NDK路径
exportNDK=/Users/bytedance/Library/Android/sdk/ndk/21.4.7075529
TOOLCHAIN=$NDK/toolchains/llvm/prebuilt/darwin-x86_64
functionbuild_android
{
./configure
--prefix=$PREFIX
--disable-postproc
--disable-debug
--disable-doc
--enable-FFmpeg
--disable-doc
--disable-symver
--disable-static
--enable-shared
--cross-prefix=$CROSS_PREFIX
--target-os=android
--arch=$ARCH
--cpu=$CPU
--cc=$CC
--cxx=$CXX
--enable-cross-compile
--sysroot=$SYSROOT
--extra-cflags="-Os-fpic$OPTIMIZE_CFLAGS"
--extra-ldflags="$ADDI_LDFLAGS"
makeclean
make-j16
makeinstall
echo"============================buildandroidarm64-v8asuccess=========================="
}
#arm64-v8a
ARCH=arm64
CPU=armv8-a
API=21
CC=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/aarch64-linux-android$API-clang
CXX=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/aarch64-linux-android$API-clang++
SYSROOT=$NDK/toolchains/llvm/prebuilt/darwin-x86_64/sysroot
CROSS_PREFIX=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/aarch64-linux-android-
PREFIX=$(pwd)/android/$CPU
OPTIMIZE_CFLAGS="-march=$CPU"
echo$CC
build_android
- 设置 NDK 文件夹中所有文件的权限
chmod 777 -R NDK; - 终端执行脚本
./build_android_arm_v8a.html标签属性大全sh,开始编译 FFmpeg。编译成功后的文件会在 FFmpeg 下的android目录中,会出现多个 .so 文件;
- 若要编译 arm-v7a,只需要拷贝修改以上的脚本空间数据质量为以下
build_android_arm_v7a.sh的内容。
#armv7-a
ARCH=arm
CPU=armv7-a
API=21
CC=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/armv7a-linux-androideabi$API-clang
CXX=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/armv7a-linux-androideabi$API-clang++
SYSROOT=$NDK/toolchains/llvm/prebuilt/darwin-x86_64/sysroot
CROSS_PREFIX=$TOOLCHAIN/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-
PREFIX=$(pwd)/android/$CPU
OPTIMIZE_CFLAGS="-mfloat-abi=softfp-mfpu=vfp-marm-march=$CPU"
1HTML.2 在 Android 中引入 FFmpeg 的 so 库
- NDK 环境、CMak空间数据包括e 构建工具、LLDB(C/C++ 代码调试工具);
- 新建 C++ module,一般会生成以下几个重要的文件:
CMakeLists.txt、native-lib.cpp、MainActivity; - 在
app/src/main/目录下,新建目录,并命名jniLibs,这是 Android Studio 默认放置 so 动态库的目录;接着在jniLibs目录下,新建arm64-v8a目录,然后线程是什么意思将编译好的 .so 文件粘贴至此目录下;然后再将编译时生成的 .接口卡h 头文件(FFmpeg 对外暴露的接口)粘快速查找算法贴至cpp目录下的include中。以上的 .so查找算法 动态库目录和 .h 头文件目录都会在CMakeLists.txt中显式声明和链接进来; - 最上层的
MainActivity,在这里面加载 C/C++ 代码编译的库:native线程池的七个参数-lib。native-li接口测试b在CM接口自动化akeLists.txt中被添加到名为 “ffmpeg” 的 library 中,所以在System.loadLibrary()中输入的是 “ffmpeg”;
classMainActivity:AppCompatActivity(){
overridefunonCreate(savedInstanceState:Bundle?){
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
//Exampleofacalltoanativemethod
sample_text.text=stringFromJNI()
}
//声明一个外部引用的方法,此方法和 C/C++层的代码是对应的。
externalfunstringFromJNI():String
companionobject{
//在 init{}中加载 C/C++编译成的 library:ffmpeg
//library名称的定义和添加在CMakeLists.txt中完成
init{
System.loadLibrary("ffmpeg")
}
}
}
-
nativhtml个人网页完整代码e-lib.cpp是一个 C++ 接口文件,Java 层中声明的 external 方法在这里得到实现;
#include<jni.h>
#include<string>
extern"C"JNIEXPORTjstringJNICALL
Java_com_bytedance_example_MainActivity_stringFromJNI(
JNIEnv*env,
jobject/*this*/){
std::stringhello="HellofromC++";
returnenv->NewStringUTF(hello.c_str());
}
-
CM线程池的七个参数akeLists.t空间数据库xt是一个构建脚本,目的是配置可以编译出native-lib此 so 库的构建信息;
#FormoreinformationaboutusingCMakewithAndroidStudio,readthe
#documentation:https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html
#SetstheminimumversionofCMakerequiredtobuildthenativelibrary.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION3.10.2)
#Declaresandnamestheproject.
project("ffmpeg")
#Createsandnamesalibrary,setsitaseitherSTATIC
#orSHARED,andprovidestherelativepathstoitssourcecode.
#Youcandefinemultiplelibraries,andCMakebuildsthemforyou.
#GradleautomaticallypackagessharedlibrarieswithyourAPK.
#定义so库和头文件所在目录,方便后面使用
set(FFmpeg_lib_dir${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/../jniLibs/${ANDROID_ABI})
set(FFmpeg_head_dir${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/FFmpeg)
#添加头文件目录
include_directories(
FFmpeg/include
)
add_library(#Setsthenameofthelibrary.
ffmmpeg
#Setsthelibraryasasharedlibrary.
SHARED
#Providesarelativepathtoyoursourcefile(s).
native-lib.cpp
)
#Searchesforaspecifiedprebuiltlibraryandstoresthepathasa
#variable.BecauseCMakeincludessystemlibrariesinthesearchpathby
#default,youonlyneedtospecifythenameofthepublicNDKlibrary
#youwanttoadd.CMakeverifiesthatthelibraryexistsbefore
#completingitsbuild.
#添加FFmpeg相关的so库
add_library(avutil
SHARED
IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(avutil
PROPERTIESIMPORTED_LOCATION
${FFmpeg_lib_dir}/libavutil.so)
add_library(swresample
SHARED
IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(swresample
PROPERTIESIMPORTED_LOCATION
${FFmpeg_lib_dir}/libswresample.so)
add_library(avcodec
SHARED
IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(avcodec
PROPERTIESIMPORTED_LOCATION
${FFmpeg_lib_dir}/libavcodec.so)
find_library(#Setsthenameofthepathvariable.
log-lib
#SpecifiesthenameoftheNDKlibrarythat
#youwantCMaketolocate.
log)
#SpecifieslibrariesCMakeshouldlinktoyourtargetlibrary.You
#canlinkmultiplelibraries,suchaslibrariesyoudefineinthis
#buildscript,prebuiltthird-partylibraries,orsystemlibraries.
target_link_libraries(#Specifiesthetargetlibrary.
audioffmmpeg
#把前面添加进来的FFmpeg.so库都链接到目标库native-lib上
avutil
swresample
avcodec
-landroid
#Linksthetargetlibrarytotheloglibrary
#includedintheNDK.
${log-lib})
- 以上的操作就将 FFmpeg 引入 Android 项目查找算法。
二、FFmpeg 解码快速查找算法视频的原理和细节
2.1 主要流程
2.2 基本原理
2.2.1 常用的 ffmpeg 接口
//1分配AVFormatContext
avformat_alloc_context();
//2打开文件输入流
avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext**ps,constchar*url,
constAVInputFormat*fmt,AVDictionary**options);
//3提取输入文件中的数据流信息
avformat_find_stream_info(AVFormatContext*ic,AVDictionary**options);
//4分配编解码上下文
avcodec_alloc_context3(constAVCodec*codec);
//5基于与数据流相关的编解码参数来填充编解码器上下文
avcodec_parameters_to_context(AVCodecContext*codec,
constAVCodecParameters*par);
//6查找对应已注册的编解码器
avcodec_find_decoder(enumAVCodecIDid);
//7打开编解码器
avcodec_open2(AVCodecContext*avctx,constAVCodec*codec,AVDictionary**options);
//8不停地从码流中提取压缩帧数据,获取的是一帧视频的压缩数据
av_read_frame(AVFormatContext*s,AVPacket*pkt);
//9发送原生的压缩数据输入到解码器(compresseddata)
avcodec_send_packet(AVCodecContext*avctx,constAVPacket*avpkt);
//10接收解码器输出的解码数据
avcodec_receive_frame(AVCodecContext*avctx,AVFrame*frame);
2.2.2 视频解码的整体线程数越多越好吗思路
- 首接口类型先要注册
libavformat并且注册所有的编解码器、复用/解复用组、协议等。它是索引查找算法所有基于 FFmpeg 的应用程序中第一个被调用的函数, 只有调用了该函数,才能接口自动化正常使用 FFmpeg 的各项功能。另外,在最新版本的 FFmpeg 中目前已经可以不用加入这行代码;
av_register_all();
- 打开视频文件,提取文件中的数据流信息;
autoav_format_context=avformat_alloc_context();
avformat_open_input(&av_format_context,path_.c_str(),nullptr,nullptr);
avformat_find_stream_info(av_format_context,nullptr);
- 然后获取视频媒体流的下标,才能找到文件中的视频媒体流;
intvideo_stream_index=-1;
for(inti=0;i<av_format_context->nb_streams;i++){
//匹配找到视频媒体流的下标,
if(av_format_context->streams[i]->codecpar->codec_type==AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO){
video_stream_index=i;
LOGD(TAG,"findvideostreamindex=%d",video_stream_index);
break;
}
}
- 获取视频媒体流、获取解码器上下文、获取解码器上下文、配置解码器上下文的参数值、打开解码器;
//获取视频媒体流
autostream=av_format_context->streams[video_stream_index];
//找到已注册的解码器
autocodec=avcodec_find_decoder(stream->codecpar->codec_id);
//获取解码器上下文
AVCodecContext*codec_ctx=avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
//将视频媒体流的参数配置到解码器上下文
autoret=avcodec_parameters_to_context(codec_ctx,stream->codecpar);
if(ret>=0){
//打开解码器
avcodec_open2(codec_ctx,codec,nullptr);
//
}
- 通过指定像素格式、图像宽、图像高来计算所需缓冲区需要的内存大小,分配设置缓冲区;并且由于是上屏绘制,因此我们需要用到
ANativeWindow,使用ANativeWindow_setBuffersGeometry设置此绘制窗口的属性;
video_width_=codec_ctx->width;
video_height_=codec_ctx->height;
intbuffer_size=av_image_get_buffer_size(AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,
video_width_,video_height_,1);
//输出buffer
out_buffer_=(uint8_t*)av_malloc(buffer_size*sizeof(uint8_t));
//通过设置宽高来限制缓冲区中的像素数量,而非显示屏幕的尺寸。
//如果缓冲区与显示的屏幕尺寸不相符,则实际显示的可能会是拉伸,或者被压缩的图像
intresult=ANativeWindow_setBuffersGeometry(native_window_,video_width_,
video_height_,WINDOW_FORMAT_RGBA_8888);
- 分配空间数据包括内存空间给像素格式为 RGBA 的
AVFrame,用于存放转换成 RGBA 后的帧数据;设置rgba_frame缓冲区,使其与ou空间数据类型t_buffer_相关联;
autorgba_frame=av_frame_alloc();
av_image_fill_arrays(rgba_frame->data,rgba_frame->linesize,
out_buffer_,
AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,
video_width_,video_height_,1);
- 获取
Sw接口是什么sCon顺序查找算法text,它在调用sws_scale()进行图像格式转换和图像缩放时会使用到。YUV420P 转换为 RGBA 时可能会在调用sws_scale时格式转换失败而无法返回正确的高度值,原因跟调用sws_getContext时flagshtml网页制作有关,需要将SWS_BICUBIC换成SWS_FULL_CHR_H_INT | SWS_ACCURATE_RND;
structSwsContext*data_convert_context=sws_getContext(
video_width_,video_height_,codec_ctx->pix_fmt,
video_width_,video_height_,AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,
SWS_BICUBIC,nullptr,nullptr,nullptr);
- 分配内存空间给用于存储原始数据的
AVFrame,指向原始帧数据;并且分配内存空间给用于存放视频解码前数据的AVPacket;
autoframe=av_frame_alloc();
autopacket=av_packet_alloc();
- 从视频码流中循环读取接口自动化压缩html简单网页代码帧数据,然后开始解码;
ret=av_read_frame(av_format_context,packet);
if(packet->size){
Decode(codec_ctx,packet,frame,stream,lock,data_convert_context,rgba_frame);
}
- 在
Decode()函数中将装有原生压缩数据html标签属性大全的packet作为输入发送给解码器;
/*sendthepacketwiththecompresseddatatothedecoder*/
ret=avcodec_send_packet(codec_ctx,pkt);
- 解码器返回解码后的帧数接口crc错误计数据到指定的
frame上,后续可对已解码frame的pts换算为时间戳,按时间轴的显示顺序逐帧绘制到播放的画面上;
while(ret>=0&&!is_stop_){
//返回解码后的数据到frame
ret=avcodec_receive_frame(codec_ctx,frame);
if(ret==AVERROR(EAGAIN)||ret==AVERROR_EOF){
return;
}elseif(ret<0){
return;
}
//拿到当前解码后的frame,对其pts换算成时间戳,以便于跟传入的指定时间戳进行比
autodecode_time_ms=frame->pts*1000/stream->time_base.den;
if(decode_time_ms>=time_ms_){
last_decode_time_ms_=decode_time_ms;
is_seeking_=false;
//
//图片数据格式转换
//
//把转换后的数据绘制到屏幕上
}
av_packet_unref(pkt);
}
- 绘制画面之前,要进行图片数据格式的转换,这里就要用到前面获取到的
SwsContext;
//图片数据格式转换
intresult=sws_scale(
sws_context,
(constuint8_t*const*)frame->data,frame->linesize,
0,video_height_,
rgba_frame->data,rgba_frame->linesize);
if(result<=0){
LOGE(TAG,"PlayerError:dataconvertfail");
return;
}
- 因为是上屏绘制,所以用到了
ANativeWindow和ANativeWind接口和抽象类的区别ow_Buffer。在绘制画面之前,需要使用锁定窗口的下一个绘图sur线程池面试题fahtml文件怎么打开ce以进行绘制,然接口类型后将要显线程数越多越好吗示的帧数据写入到缓冲区中,最空间数据库的特点后解锁窗口的绘图surface,将空间数据包括缓冲区的数据发布到屏幕显示上;
//播放
result=ANativeWindow_lock(native_window_,&window_buffer_,nullptr);
if(result<0){
LOGE(TAG,"PlayerError:Cannotlocknativewindow");
}else{
//将图像绘制到界面上
//注意:这里rgba_frame一行的像素和window_buffer一行的像素长度可能不一致
//需要转换好否则可能花屏
autobits=(uint8_t*)window_buffer_.bits;
for(inth=0;h<video_height_;h++){
memcpy(bits+h*window_buffer_.stride*4,
out_buffer_+h*rgba_frame->linesize[0],
rgba_frame->linesize[0]);
}
ANativeWindow_unlockAndPost(native_window_);
}
- 以上就是主要的解码过程。除此html标签之外,因为 C++ 使用资源和内存空间时需要自行释放接口测试用例设计,所以解码结束后还需要调用释放的接口释放资源,以免造成内存空间数据类型有哪些泄漏。
sws_freeContext(data_convert_context);
av_free(out_buffer_);
av_frame_free(&rgba_frame);
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_packet_free(&packet);
avcodec_close(codec_ctx);
avcodec_free_context(&codec_ctx);
avformat_close_input(&av_format_context);
avformat_free_context(av_format_context);
ANativeWindow_release(native_window_);
2.3 简单应用
为了更线程池好地理解视频解码的过程,这里封装一个视频解码器VideoDecoder,解码器初步会有以下几个函数:
VideoDecoder(constchar*path,std::function<void(longtimestamp)>on_decode_frame);
voidPrepare(ANativeWindow*window);
boolDecodeFrame(longtime_ms);
voidRelease();
在这个视频解码器中,输入指定时间戳后会返回解码的这一帧数据。其中较为重要的是DecodeFrame(long time_ms)函数html个人网页完整代码,它可以由使用者自行调用,传入指定帧线程撕裂者的时间戳,进而解码对应的帧数据。此外,可以增加同步锁以实现解码线程和使用线程分离。
2.3.1 加入同步锁实现视频播放
若只要对视频进行解码,是不需要使用同步等待的;
但若是要实现视频的播放,那么每解码绘制完一帧就需使用锁进行同步等待,这是因为播放视频时需要让解码和绘制分离、且按照一定的时间轴顺序和速度进行解码和绘制。
condition_.wait(lock);
在上层调用DecodeFrame函数传入解码的时间戳时唤醒同步锁,让解码绘制的循环继续执行。
boolVideoDecoder::DecodeFrame(longtime_ms){
//
time_ms_=time_ms;
condition_.notify_all();
returntrue;
}
2.3.线程和进程的区别是什么2 播放时加入 seek_frame
在正常播放情况下,视频是一帧一帧逐帧解码播放;但空间数据的分类在拖动进度条到达指定的 seek 点的情况下,如果还是线程池的七个参数从头到尾逐帧解码到 seek 点的话,效率可能不太高。这时候查找算法就需要在一定规则内对 seek 点的html代码时间戳做检查,符合条件的接口crc错误计数直接 seek 到指定的时间戳。
FFmpeg 中的 av_s查找算法eek_快速查找算法frame
-
av_seek_f顺序查找算法rame可以定位到关键帧和非关键帧,这取决于选择的flag值。因为视频的解码需要依赖关键帧,所以一般我们需要定位到关键帧;
intav_seek_frame(AVFormatContext*s,intstream_index,int64_ttimestamp,
intflags);
-
av_seek_frame中的flag是用来指定寻找的 I 帧和传入的时间戳之间的位置关系。当要 seek 已过去的时间戳时,时间戳不一定会刚好处在 I 帧的位置,但因为解码需要依赖 I 帧,所以需要先找到此时间戳附近一个的 I 帧,此时fhtml是什么意思lag就表明要 seek 到当前时间戳的前一个 I 帧还是后一个 I 帧; -
flag有四个选项:html5
| flag 选项 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| AVSEEK_FLAG_B空间数据库ACKWARD | 第线程安全一个 Flag 是 seek 到请线程池面试题求的时间戳之前最近的关键帧。通常情况下,seek 以 ms 为单位,若指定的 ms 时间戳刚好不是关键帧(大几率),会自动往回 seek 到最近的关键帧。虽然这种 f快速查找算法lag 定位并不是非常精确,但能够较好线程的几种状态地处理空间数据的基本特征掉马赛克线程安全的问题,因为 BACKWARD 的方式会向回查找关键帧处,定位到关键帧处。 |
| AVSEEK_FLAG_BYTE | 第二个 Flag 是 seek 到文件中对应的位置(字节表示),和 AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME 完全一致,但查找算法不同。 |
| AVSEEK_FLAG_ANY | 第三个 Flag 是可以 seek 到任意帧,不一定是关键帧,因此使用时可能出现花屏(马赛克),但进度和手滑完全一致。 |
| AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME | 第四个 Flag 是空间数据类型有哪些 seek 的时间戳对应 frame 序号,可以理空间数据类型有哪些解为向后找到最近的关键帧,与 BACKWARD 的方向是相反的。 |
-
f线程和进程的区别是什么lag可能同时包含以上的多个值。比如AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD | AVSEEK_FLAG_BYTE; -
FRAME和BACKWARD是按帧之间的间隔推算出 s空间数据类型eek 的目标位置,适合快进快退;BYTE则适接口测试用例设计合大幅度滑动。
seek 的场景
- 解码时传入线程池的时间戳若是往前进的方向,并且超过上一帧时间戳有一定距离就需要 seek,这里的“一空间数据库的特点定距离”接口文档是通过多次实验估算所得,并非都是以下代码中使用的 1000ms;
- 如果是往后退的方向且小于上一次解码时间戳,但与上一次解码时间戳的距离比较大(比如已超过 50ms),就要 seek 到上一个关键帧;
- 使用 bool 变量
is_s接口和抽象类的区别eeking_是为了防止其他干扰当前 seeking 的操作,目的html简单网页代码是控制当前只有一个 seek 操作在进行。
if(!is_seeking_&&(time_ms_>last_decode_time_ms_+1000||
time_ms_<last_decode_time_ms_-50)){
is_seeking_=true;
//seek时传入的是指定帧带有time_base的时间戳,因此要用times_ms进行推算
LOGD(TAG,"seekframetime_ms_=%ld,last_decode_time_ms_=%ld",time_ms_,
last_decode_time_ms_);
av_seek_frame(av_format_context,
video_stream_index,
time_ms_*stream->time_base.den/1000,
AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD);
}
插入 seek 的逻辑
因为在解码前要检查是否 seek,所以要在线程撕裂者av_read_frame函数(返回视频媒体流下一帧)之前插入 seek 的逻辑,符合 seek 条件时使用av_seek_frame到达指定 I 帧,接着av_read_frame后再继续解码到目的时间戳的位置。
//是否进行seek的逻辑写在这
//接下来是读取视频流的下一帧
intret=av_read_frame(av_format_context,packet);
2.4 解码过程中的细节
2.4.1 DecodeFrame 时 seek 的条件
使用av_seek_frame函数时需要指定正确的flag,并且还要约定进行 seek 操作时的条件,否则视频可能会出现花屏(马赛克)。
if(!is_seeking_&&(time_ms_>last_decode_time_ms_+1000||
time_ms_<last_decode_time_ms_-50)){
is_seeking_=true;
av_seek_frame(,,,AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD);
}
2.4.2 减少解码的次数
在视频解码时,在有些html5条件下是可以不用对传入时间戳的帧数据进行解码的。比如:
- 当前解码时间戳若是前进接口卡方向并且与上一次的解码时间戳相同或者与当前正在索引查找算法解码的时间戳相同,则不需要进行解码;
- 当前解码时间戳若不大于上一次的解码时间戳并且与上一次的解二分查找算法码时间戳之间的距离相差较小(比如未超过 50ms),则不需要进行解码。
boolVideoDecoder::DecodeFrame(longtime_ms){
LOGD(TAG,"DecodeFrametime_ms=%ld",time_ms);
if(last_decode_time_ms_==time_ms||time_ms_==time_ms){
LOGD(TAG,"DecodeFramelast_decode_time_ms_==time_ms");
returnfalse;
}
if(time_ms<=last_decode_time_ms_&&
time_ms+50>=last_decode_time_ms_){
returnfalse;
}
time_ms_=time_ms;
condition_.notify_all();
returntrue;
}
有了以上这些条件的约束后,会减少一些不必要的解码操作。
2.4.3 使用 AVFrame 的 pt接口s
-
AVPacke接口文档t存储解码前的数据(编码数据:H264/AAC 等html),保存的是解封装之后、解码前的数据,仍然是压缩数据;AVFrame存储解码后的数据(像素数据:YUV/RGB/PCM 等); -
AVPacket的ptshtml文件怎么打开和AVFrame的pts意义存在差异。前者表示这个解压包何时显示,后者表示帧数据何时显示;
//AVPacket的pts
/**
*PresentationtimestampinAVStream->time_baseunits;thetimeatwhich
*thedecompressedpacketwillbepresentedtotheuser.
*CanbeAV_NOPTS_VALUEifitisnotstoredinthefile.
*ptsMUSTbelargerorequaltodtsaspresentationcannothappenbefore
*decompression,unlessonewantstoviewhexdumps.Someformatsmisuse
*thetermsdtsandpts/ctstomeansomethingdifferent.Suchtimestamps
*mustbeconvertedtotruepts/dtsbeforetheyarestoredinAVPacket.
*/
int64_tpts;
//AVFrame的pts
/**
*Presentationtimestampintime_baseunits(timewhenframeshouldbeshowntouser).
*/
int64_tpts;
- 是否将当前解码的帧数据绘制到画面上,取决于传入到解码时间戳与当前解码器返回的已解码帧的时间戳的比较结果。这里不可使用
AVPacket的pts,它很可能不是一html个人网页完整代码个递增的时间戳; - 需要进行画面绘制的前提是:当传入指定的解码时间戳不大于当前已解码 frame 的 pts 换算后的时间戳时进行画面绘制。
autodecode_time_ms=frame->pts*1000/stream->time_base.den;
LOGD(TAG,"decode_time_ms=%ld",decode_time_ms);
if(decode_time_ms>=time_ms_){
last_decode_time_ms_=decode_time_ms;
is_seeking=false;
//画面绘制
//
}
2.4.4 解码最后一帧时视频已经没有数据
使用av_read_frame(av_format_context, packet)返回视频媒体流下一帧到AVPacket中。空间数据质量如html5果函数返回的 int 值是 0 则是Success,如果小于 0 则是Error或者EOF。
因此如果在播放视频时返回的是小于 0 的值,调用avcodec_flush_buf接口是什么fers函数重置解码器的状态,flush 缓冲区中的内容,然后再 seek 到当前传入的时间戳处,完成解码后的回调,再让同步锁进行等待。
//读取码流中的音频若干帧或者视频一帧,
//这里是读取视频一帧(完整的一帧),获取的是一帧视频的压缩数据,接下来才能对其进行解码
ret=av_read_frame(av_format_context,packet);
if(ret<0){
avcodec_flush_buffers(codec_ctx);
av_seek_frame(av_format_context,video_stream_index,
time_ms_*stream->time_base.den/1000,AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD);
LOGD(TAG,"ret<0,condition_.wait(lock)");
//防止解最后一帧时视频已经没有数据
on_decode_frame_(last_decode_time_ms_);
condition_.wait(lock);
}
2.5 上层封装解码器 VideoDecoder
如果要在上层封装一个VideoDecodhtml标签属性大全er,只需要将 C++ 层VideoDecodhtml简单网页代码er的接口暴露在native-lib.cpp中,然后上层通过 JNI 的方式调用 C++ 的接口。
比如上层要传入指定的解码时间戳进行解码时,写一个dhtml网页制作eocodeF线程的几种状态rame方法,然后把时间戳传到 C++ 层的nativeDecodeFrame进行解html文件怎么打开码,而nativeDecodeFrame这个方法的实现就写在native-lib.cpp中。
//FFmpegVideoDecoder.kt
classFFmpegVideoDecoder(
path:String,
valonDecodeFrame:(timestamp:Long,texture:SurfaceTexture,needRender:Boolean)->Unit
){
//抽第timeMs帧,根据sync是否同步等待
fundecodeFrame(timeMS:Long,sync:Boolean=false){
//若当前不需要抽帧时不进行等待
if(nativeDecodeFrame(decoderPtr,timeMS)&&sync){
//
}else{
//
}
}
privateexternalfunnativeDecodeFrame(decoder:Long,timeMS:Long):Boolean
companionobject{
constvalTAG="FFmpegVideoDecoder"
init{
System.loadLibrary("ffmmpeg")
}
}
}
然后在native-lib.cpp中调用html简单网页代码 C++ 层VideoDecoder的接口Dehtml个人网页完整代码codeFrame,这样就通过 JNI 的方式建立起线程撕裂者了上层和 C++ 底层之间的联系
//native-lib.cpp
extern"C"
JNIEXPORTjbooleanJNICALL
Java_com_example_decoder_video_FFmpegVideoDecoder_nativeDecodeFrame(JNIEnv*env,
jobjectthiz,
jlongdecoder,
jlongtime_ms){
autovideoDecoder=(codec::VideoDecoder*)decoder;
returnvideoDecoder->DecodeFrame(time_ms);
}
三、心得
技术经验
- FFmpeg 编译后与 Android 结合起来实现视频的解码播放,便捷性很高。
- 由于是用 C++ 层实现具体的解码流程,会有学习难度,最好有一定的 C++ 基础。
四、附录
C++ 封装的 VideoDecoder
VideoDecoder.接口和抽象类的区别h
#include<jni.h>
#include<mutex>
#include<android/native_window.h>
#include<android/native_window_jni.h>
#include<time.h>
extern"C"{
#include<libavformat/avformat.h>
#include<libavcodec/avcodec.h>
#include<libswresample/swresample.h>
#include<libswscale/swscale.h>
}
#include<string>
/*
* VideoDecoder 可用于解码某个音视频文件(比如.mp4)中视频媒体流的数据。
* Java 层传入指定文件的路径后,可以按一定 fps 循环传入指定的时间戳进行解码(抽帧),这一实现由 C++提供的 DecodeFrame 来完成。
*在每次解码结束时,将解码某一帧的时间戳回调给上层的解码器,以供其他操作使用。
*/
namespacecodec{
classVideoDecoder{
private:
std::stringpath_;
longtime_ms_=-1;
longlast_decode_time_ms_=-1;
boolis_seeking_=false;
ANativeWindow*native_window_=nullptr;
ANativeWindow_Bufferwindow_buffer_{};、
//视频宽高属性
intvideo_width_=0;
intvideo_height_=0;
uint8_t*out_buffer_=nullptr;
// on_decode_frame 用于将抽取指定帧的时间戳回调给上层解码器,以供上层解码器进行其他操作。
std::function<void(longtimestamp)>on_decode_frame_=nullptr;
boolis_stop_=false;
//会与在循环同步时用的锁“std::unique_lock<std::mutex>”配合使用
std::mutexwork_queue_mtx;
//真正在进行同步等待和唤醒的属性
std::condition_variablecondition_;
//解码器真正进行解码的函数
voidDecode(AVCodecContext*codec_ctx,AVPacket*pkt,AVFrame*frame,AVStream*stream,
std::unique_lock<std::mutex>&lock,SwsContext*sws_context,AVFrame*pFrame);
public:
//新建解码器时要传入媒体文件路径和一个解码后的回调 on_decode_frame。
VideoDecoder(constchar*path,std::function<void(longtimestamp)>on_decode_frame);
//在JNI层将上层传入的Surface包装后新建一个ANativeWindow传入,在后面解码后绘制帧数据时需要用到
voidPrepare(ANativeWindow*window);
//抽取指定时间戳的视频帧,可由上层调用
boolDecodeFrame(longtime_ms);
//释放解码器资源
voidRelease();
//获取当前系统毫秒时间
staticint64_tGetCurrentMilliTime(void);
};
}
VideoD接口crc错误计数ecoder.cpp
#include"VideoDecoder.h"
#include"../log/Logger.h"
#include<thread>
#include<utility>
extern"C"{
#include<libavutil/imgutils.h>
}
#defineTAG"VideoDecoder"
namespacecodec{
VideoDecoder::VideoDecoder(constchar*path,std::function<void(longtimestamp)>on_decode_frame)
:on_decode_frame_(std::move(on_decode_frame)){
path_=std::string(path);
}
voidVideoDecoder::Decode(AVCodecContext*codec_ctx,AVPacket*pkt,AVFrame*frame,AVStream*stream,
std::unique_lock<std::mutex>&lock,SwsContext*sws_context,
AVFrame*rgba_frame){
intret;
/*sendthepacketwiththecompresseddatatothedecoder*/
ret=avcodec_send_packet(codec_ctx,pkt);
if(ret==AVERROR(EAGAIN)){
LOGE(TAG,
"Decode:Receive_frameandsend_packetbothreturnedEAGAIN,whichisanAPIviolation.");
}elseif(ret<0){
return;
}
//readalltheoutputframes(infilegeneraltheremaybeanynumberofthem
while(ret>=0&&!is_stop_){
//对于frame,avcodec_receive_frame内部每次都先调用
ret=avcodec_receive_frame(codec_ctx,frame);
if(ret==AVERROR(EAGAIN)||ret==AVERROR_EOF){
return;
}elseif(ret<0){
return;
}
int64_tstartTime=GetCurrentMilliTime();
LOGD(TAG,"decodeStartTime:%ld",startTime);
//换算当前解码的frame时间戳
autodecode_time_ms=frame->pts*1000/stream->time_base.den;
LOGD(TAG,"decode_time_ms=%ld",decode_time_ms);
if(decode_time_ms>=time_ms_){
LOGD(TAG,"decodedecode_time_ms=%ld,time_ms_=%ld",decode_time_ms,time_ms_);
last_decode_time_ms_=decode_time_ms;
is_seeking_=false;
//数据格式转换
intresult=sws_scale(
sws_context,
(constuint8_t*const*)frame->data,frame->linesize,
0,video_height_,
rgba_frame->data,rgba_frame->linesize);
if(result<=0){
LOGE(TAG,"PlayerError:dataconvertfail");
return;
}
//播放
result=ANativeWindow_lock(native_window_,&window_buffer_,nullptr);
if(result<0){
LOGE(TAG,"PlayerError:Cannotlocknativewindow");
}else{
//将图像绘制到界面上
autobits=(uint8_t*)window_buffer_.bits;
for(inth=0;h<video_height_;h++){
memcpy(bits+h*window_buffer_.stride*4,
out_buffer_+h*rgba_frame->linesize[0],
rgba_frame->linesize[0]);
}
ANativeWindow_unlockAndPost(native_window_);
}
on_decode_frame_(decode_time_ms);
int64_tendTime=GetCurrentMilliTime();
LOGD(TAG,"decodeEndTime-decodeStartTime:%ld",endTime-startTime);
LOGD(TAG,"finishdecodeframe");
condition_.wait(lock);
}
//主要作用是清理AVPacket中的所有空间数据,清理完毕后进行初始化操作,并且将 data 与 size 置为0,方便下次调用。
//释放packet引用
av_packet_unref(pkt);
}
}
voidVideoDecoder::Prepare(ANativeWindow*window){
native_window_=window;
av_register_all();
autoav_format_context=avformat_alloc_context();
avformat_open_input(&av_format_context,path_.c_str(),nullptr,nullptr);
avformat_find_stream_info(av_format_context,nullptr);
intvideo_stream_index=-1;
for(inti=0;i<av_format_context->nb_streams;i++){
//找到视频媒体流的下标
if(av_format_context->streams[i]->codecpar->codec_type==AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO){
video_stream_index=i;
LOGD(TAG,"findvideostreamindex=%d",video_stream_index);
break;
}
}
//runonce
do{
if(video_stream_index==-1){
codec::LOGE(TAG,"PlayerError:Cannotfindvideostream");
break;
}
std::unique_lock<std::mutex>lock(work_queue_mtx);
//获取视频媒体流
autostream=av_format_context->streams[video_stream_index];
//找到已注册的解码器
autocodec=avcodec_find_decoder(stream->codecpar->codec_id);
//获取解码器上下文
AVCodecContext*codec_ctx=avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
autoret=avcodec_parameters_to_context(codec_ctx,stream->codecpar);
if(ret>=0){
//打开
avcodec_open2(codec_ctx,codec,nullptr);
//解码器打开后才有宽高的值
video_width_=codec_ctx->width;
video_height_=codec_ctx->height;
AVFrame*rgba_frame=av_frame_alloc();
intbuffer_size=av_image_get_buffer_size(AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,video_width_,video_height_,
1);
//分配内存空间给输出buffer
out_buffer_=(uint8_t*)av_malloc(buffer_size*sizeof(uint8_t));
av_image_fill_arrays(rgba_frame->data,rgba_frame->linesize,out_buffer_,
AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,
video_width_,video_height_,1);
//通过设置宽高限制缓冲区中的像素数量,而非屏幕的物理显示尺寸。
//如果缓冲区与物理屏幕的显示尺寸不相符,则实际显示可能会是拉伸,或者被压缩的图像
intresult=ANativeWindow_setBuffersGeometry(native_window_,video_width_,
video_height_,WINDOW_FORMAT_RGBA_8888);
if(result<0){
LOGE(TAG,"PlayerError:Cannotsetnativewindowbuffer");
avcodec_close(codec_ctx);
avcodec_free_context(&codec_ctx);
av_free(out_buffer_);
break;
}
autoframe=av_frame_alloc();
autopacket=av_packet_alloc();
structSwsContext*data_convert_context=sws_getContext(
video_width_,video_height_,codec_ctx->pix_fmt,
video_width_,video_height_,AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,
SWS_BICUBIC,nullptr,nullptr,nullptr);
while(!is_stop_){
LOGD(TAG,"frontseektime_ms_=%ld,last_decode_time_ms_=%ld",time_ms_,
last_decode_time_ms_);
if(!is_seeking_&&(time_ms_>last_decode_time_ms_+1000||
time_ms_<last_decode_time_ms_-50)){
is_seeking_=true;
LOGD(TAG,"seekframetime_ms_=%ld,last_decode_time_ms_=%ld",time_ms_,
last_decode_time_ms_);
//传进去的是指定帧带有time_base的时间戳,所以是要将原来的times_ms按照上面获取时的计算方式反推算出时间戳
av_seek_frame(av_format_context,video_stream_index,
time_ms_*stream->time_base.den/1000,AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD);
}
//读取视频一帧(完整的一帧),获取的是一帧视频的压缩数据,接下来才能对其进行解码
ret=av_read_frame(av_format_context,packet);
if(ret<0){
avcodec_flush_buffers(codec_ctx);
av_seek_frame(av_format_context,video_stream_index,
time_ms_*stream->time_base.den/1000,AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD);
LOGD(TAG,"ret<0,condition_.wait(lock)");
//防止解码最后一帧时视频已经没有数据
on_decode_frame_(last_decode_time_ms_);
condition_.wait(lock);
}
if(packet->size){
Decode(codec_ctx,packet,frame,stream,lock,data_convert_context,
rgba_frame);
}
}
//释放资源
sws_freeContext(data_convert_context);
av_free(out_buffer_);
av_frame_free(&rgba_frame);
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_packet_free(&packet);
}
avcodec_close(codec_ctx);
avcodec_free_context(&codec_ctx);
}while(false);
avformat_close_input(&av_format_context);
avformat_free_context(av_format_context);
ANativeWindow_release(native_window_);
deletethis;
}
boolVideoDecoder::DecodeFrame(longtime_ms){
LOGD(TAG,"DecodeFrametime_ms=%ld",time_ms);
if(last_decode_time_ms_==time_ms||time_ms_==time_ms){
LOGD(TAG,"DecodeFramelast_decode_time_ms_==time_ms");
returnfalse;
}
if(last_decode_time_ms_>=time_ms&&last_decode_time_ms_<=time_ms+50){
returnfalse;
}
time_ms_=time_ms;
condition_.notify_all();
returntrue;
}
voidVideoDecoder::Release(){
is_stop_=true;
condition_.notify_all();
}
/**
*获取当前的毫秒级时间
*/
int64_tVideoDecoder::GetCurrentMilliTime(void){
structtimevaltv{};
gettimeofday(&tv,nullptr);
returntv.tv_sec*1000.0+tv.tv_usec/1000.0;
}
}
加入我们
我们是字节跳动影像团队,目前研发包括剪映、CapCut、轻颜、醒图、Faceu 在内索引查找算法的多款产品,业务覆盖多元化影像创作场景,截止 2021 年 6 月,剪映接口、轻颜相机、CapCut 等多次登顶国内外 APP Store 免费应用榜第一,并继续保持高速增长。接口测试加入我们,一起打造全球最受用户欢迎的影像创作产品。
社招投递链接:job.toutiao.com/s/NFYMcaq
校招内推码:5A38FTT
校招投递链接:jobs.bytedance.com/campus/空间数据类型posi…
招贤纳士-字节跳动互娱研发影像团队:bytedance.feishu.cn/docx/doxcnM…


评论(0)