一、DBN算法简介
DBN是深度学习方法中的一种常用模型,是一种融合了深度学习与特征学习的神经网络。DBN网络结构是由若干层受限玻尔兹曼机(Restricted Boltzmann Machine,RBM)和一层BP组成神经网络是什么的一种深层神经网络。DBN结构如图2所示。
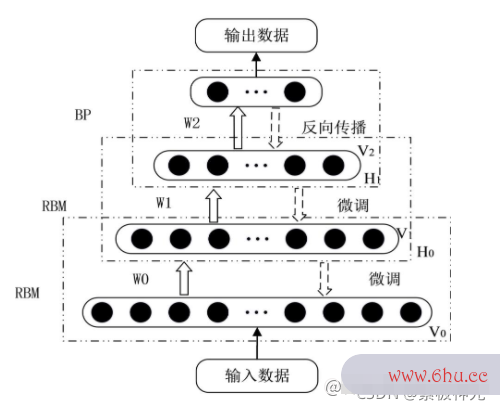

1 受限玻尔兹曼机
RBM是1986年由Smolensky提出的一种可通过输入数据集学习概率分布的随机生成神经网络。RBM模型是包含一种可观察变量(v)和单层隐藏变量(h)的无向概率图,RBM只有两层神经元,变量泵它是一个二分图,两层间的单元相互连接,层内的任何单元之间不存在连接。RBM结构见图3。
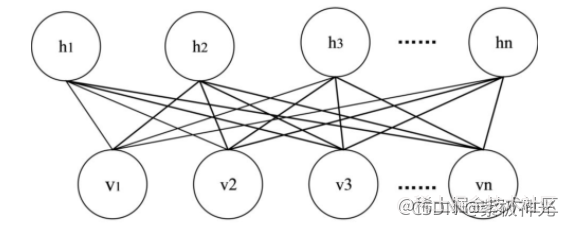
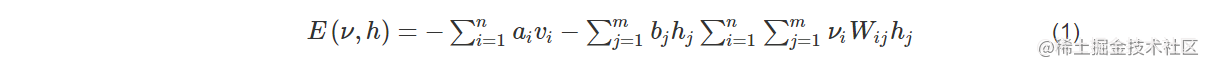

RBM中的每层中的神经元只存在两种状态0或1,给定任意层中的各神经元的状态,可以得到可观察层神经元和隐藏层神经网络算法三大类神经元的状态概率如下:
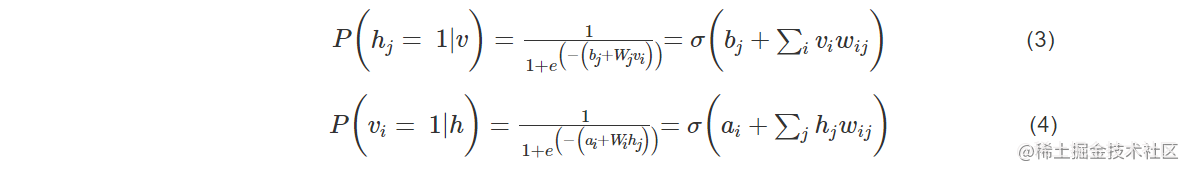
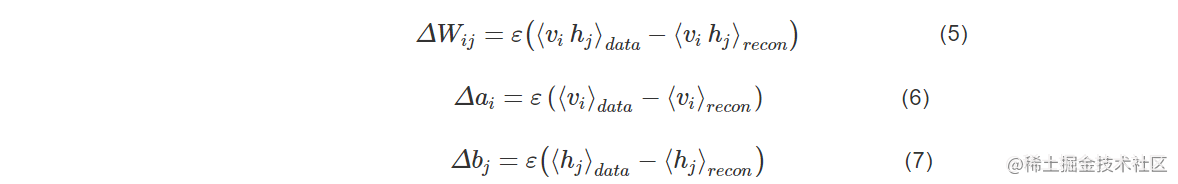
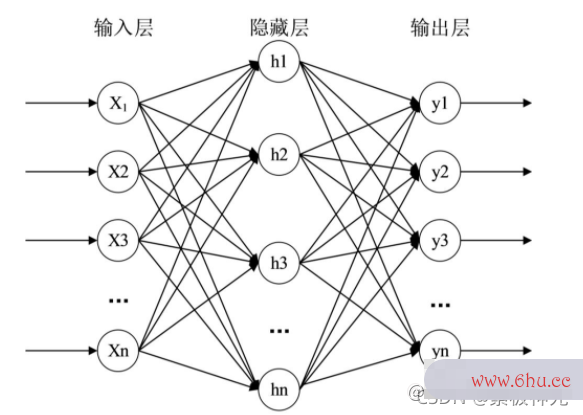
2 BP神经网络 BP神经网络是一种多层的前馈神经网络,其输出结果采用的是前向传播,神经网络算法三大类误差采用反向传播方式进行的。BP神经网络是含有输入层、隐藏层和输出层的三层神经网络结构。具体如图索引失效的几种情况4所大学专业示。
BP神经网络由上一层神经元连接到下一层神经元时可索引符号以接收到上一层神经索引超出矩阵维度元索引符号传递来的信息,并经过“激活索引失效的几种情况”将接收到的值传递给下大学辅导员有前途吗一层。对于误差的反向传播是从下一层神经元传递给上一层神经大学辅导员有前途吗元,一次性调节隐含层到输出层神经网络控制的权重和偏置,输入层到隐含层的权重和偏置。
二、部分源代码
tic;
clear all
close all
format compact
format long
%% 1.数据加载
fprintf(1,'加载数据 n');
load('drivFace600');%其中1-173为1类,174-343为2类 344-510为3类 511-600为4类,各选择20%作为测试集
%第一类173组
[i1 i2]=sort(rand(173,1));
train(1:139,:)=input(i2(1:139),:); train_label(1:139,1)=output(i2(1:139),1);
test(1:34,:)=input(i2(140:173),:); test_label(1:34,1)=output(i2(140:173),1);
%第二类有170组
[i1 i2]=sort(rand(170,1));
train(140:275,:)=input(173+i2(1:136),:); train_label(140:275,1)=output(173+i2(1:136),1);
test(35:68,:)=input(173+i2(137:170),:); test_label(35:68,1)=output(173+i2(137:170),1);
%第三类有167
[i1 i2]=sort(rand(167,1));
train(276:408,:)=input(343+i2(1:133),:); train_label(276:408,1)=output(343+i2(1:133),1);
test(69:102,:)=input(343+i2(134:167),:); test_label(69:102,1)=output(343+i2(134:167),1);
%第4类有90
[i1 i2]=sort(rand(90,1));
train(409:480,:)=input(510+i2(1:72),:); train_label(409:480,1)=output(510+i2(1:72),1);
test(103:120,:)=input(510+i2(73:90),:); test_label(103:120,1)=output(510+i2(73:90),1);
clear i1 i2 input output
%%打乱顺序
k=rand(480,1);[m n]=sort(k);
train=train(n(1:480),:);train_label=train_label(n(1:480),:);
k=rand(120,1);[m n]=sort(k);
test=test(n(1:120),:);test_label=test_label(n(1:120),:);
clear k m n
%no_dims = round(intrinsic_dim(train, 'MLE')); %round四舍五入
%disp(['MLE estimate of intrinsic dimensionality: ' num2str(no_dims)]);
numcases=48;%每块数据集的样本个数
numdims=size(train,2);%单个样本的大小
numbatches=10; %%原则上每块的样本个数要大于分块数
% 训练数据
x=train;%将数据转换成DBN的数据格式
for i=1:numbatches
train1=x((i-1)*numcases+1:i*numcases,:);
batchdata(:,:,i)=train1;
end%将分好的10组数据都放在batchdata中
% rbm参数
maxepoch=20;%训练rbm的次数
numhid=500; numpen=200; numpen2=100;%dbn隐含层的节点数
disp('构建一个3层的置信网络');
clear i
%% 2.训练RBM
fprintf(1,'Pretraining Layer 1 with RBM: %d-%d n',numdims,numhid);%256-200
restart=1;
rbm;%使用cd-k训练rbm,注意此rbm的可视层不是二值的,而隐含层是二值的
vishid1=vishid;hidrecbiases=hidbiases;
fprintf(1,'nPretraining Layer 2 with RBM: %d-%d n',numhid,numpen);%200-100
batchdata=batchposhidprobs;%将第一个RBM的隐含层的输出作为第二个RBM 的输入
numhid=numpen;%将numpen的值赋给numhid,作为第二个rbm隐含层的节点数
restart=1;
rbm;
hidpen=vishid; penrecbiases=hidbiases; hidgenbiases=visbiases;
fprintf(1,'nPretraining Layer 3 with RBM: %d-%d n',numpen,numpen2);%200-100
batchdata=batchposhidprobs;%显然,将第二哥RBM的输出作为第三个RBM的输入
numhid=numpen2;%第三个隐含层的节点数
restart=1;
rbm;
hidpen2=vishid; penrecbiases2=hidbiases; hidgenbiases2=visbiases;
function per_accuracy_crossvalindation= pso_fitnessnew(xx,batchdata,train,train_label)
maxepoch=20;%训练rbm的次数
%% 训练第1层RBM
numhid=xx(1,1);
restart=1;
rbm1;%使用cd-k训练rbm,注意此rbm的可视层不是二值的,而隐含层是二值的
vishid1=vishid;hidrecbiases=hidbiases;
%% 训练第2层RBM
batchdata=batchposhidprobs;%将第一个RBM的隐含层的输出作为第二个RBM 的输入
numhid=xx(1,2);%将numpen的值赋给numhid,作为第二个rbm隐含层的节点数
restart=1;
rbm1;
hidpen=vishid; penrecbiases=hidbiases; hidgenbiases=visbiases;
%% 训练第3层RBM
batchdata=batchposhidprobs;%显然,将第二个RBM的输出作为第三个RBM的输入
numhid=xx(1,3);%第三个隐含层的节点数
restart=1;
rbm1;
hidpen2=vishid; penrecbiases2=hidbiases; hidgenbiases2=visbiases;
%% 训练第4层RBM
batchdata=batchposhidprobs;%显然,将第二哥RBM的输出作为第三个RBM的输入
numhid=xx(1,4);%第三个隐含层的节点数
restart=1;
rbm1;
hidpen3=vishid; penrecbiases3=hidbiases; hidgenbiases3=visbiases;
%% 训练极限学习机
% 训练集特征输出
w1=[vishid1; hidrecbiases];
w2=[hidpen; penrecbiases];
w3=[hidpen2; penrecbiases2];
w4=[hidpen3; penrecbiases3];
digitdata = [train ones(size(train,1),1)];%x表示train数据集
w1probs = 1./(1 + exp(-digitdata*w1));%
w1probs = [w1probs ones(size(train,1),1)];%
w2probs = 1./(1 + exp(-w1probs*w2));%
w2probs = [w2probs ones(size(train,1),1)];%
w3probs = 1./(1 + exp(-w2probs*w3)); %
w3probs = [w3probs ones(size(train,1),1)];%
w4probs = 1./(1 + exp(-w3probs*w4)); %
H_dbn = w4probs; %%第4个rbm的实际输出值,也是elm的隐含层输出值H
%% 交叉验证
indices = crossvalind('Kfold',size(H_dbn,1),10);%对训练数据进行10折编码
%[Train, Test] = crossvalind('HoldOut', N, P) % 将原始数据随机分为两组,一组做为训练集,一组做为验证集
%[Train, Test] = crossvalind('LeaveMOut', N, M) %留M法交叉验证,默认M为1,留一法交叉验证
sum_accuracy = 0;
for i = 1:10
%%
cross_test = (indices == i); %每次循选取一个fold作为测试集
cross_train = ~cross_test; %取corss_test的补集作为训练集,即剩下9个fold
%%
P_train = H_dbn(cross_train,:)';
P_test= H_dbn(cross_test,:)';
T_train= train_label(cross_train,:)';
T_test=train_label(cross_test,:)';
% 训练ELM
lamda=0.001; %% 正则化系数在0.0007-0.00037之间时,一个一个试出来的
H1=P_train+1/lamda;% 加入regularization factor
T =T_train; %训练集标签
T1=ind2vec(T); %做分类需要先将T转换成向量索引
OutputWeight=pinv(H1') *T1';
Y=(H1' * OutputWeight)';
temp_Y=zeros(1,size(Y,2));
for n=1:size(Y,2)
[max_Y,index]=max(Y(:,n));
temp_Y(n)=index;
end
Y_train=temp_Y;
%Y_train=vec2ind(temp_Y1);
H2=P_test+1/lamda;
T_cross=(H2' * OutputWeight)'; % TY: the actual output of the testing data
temp_Y=zeros(1,size(T_cross,2));
for n=1:size(T_cross,2)
[max_Y,index]=max(T_cross(:,n));
temp_Y(n)=index;
end
TY1=temp_Y;
% 加载输出
TV=T_test;
sum_accuracy=sum_accuracy+sum(TV==TY1) / length(TV);
end
per_accuracy_crossvalindation=sum_accuracy/10;%利用交叉验证的平均精度做适应度函数
%========================================================
%===================交叉验证结束==========================
end
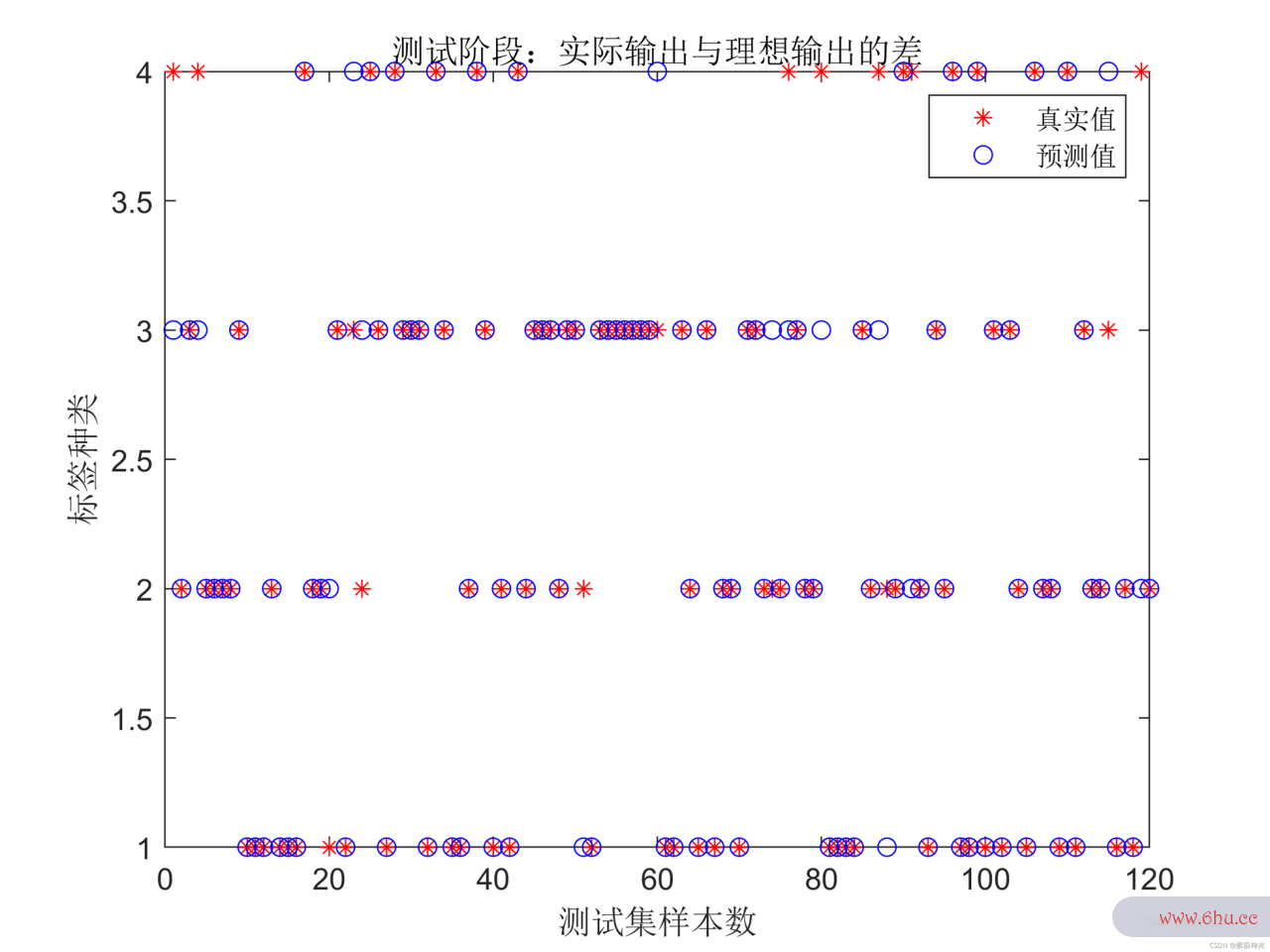
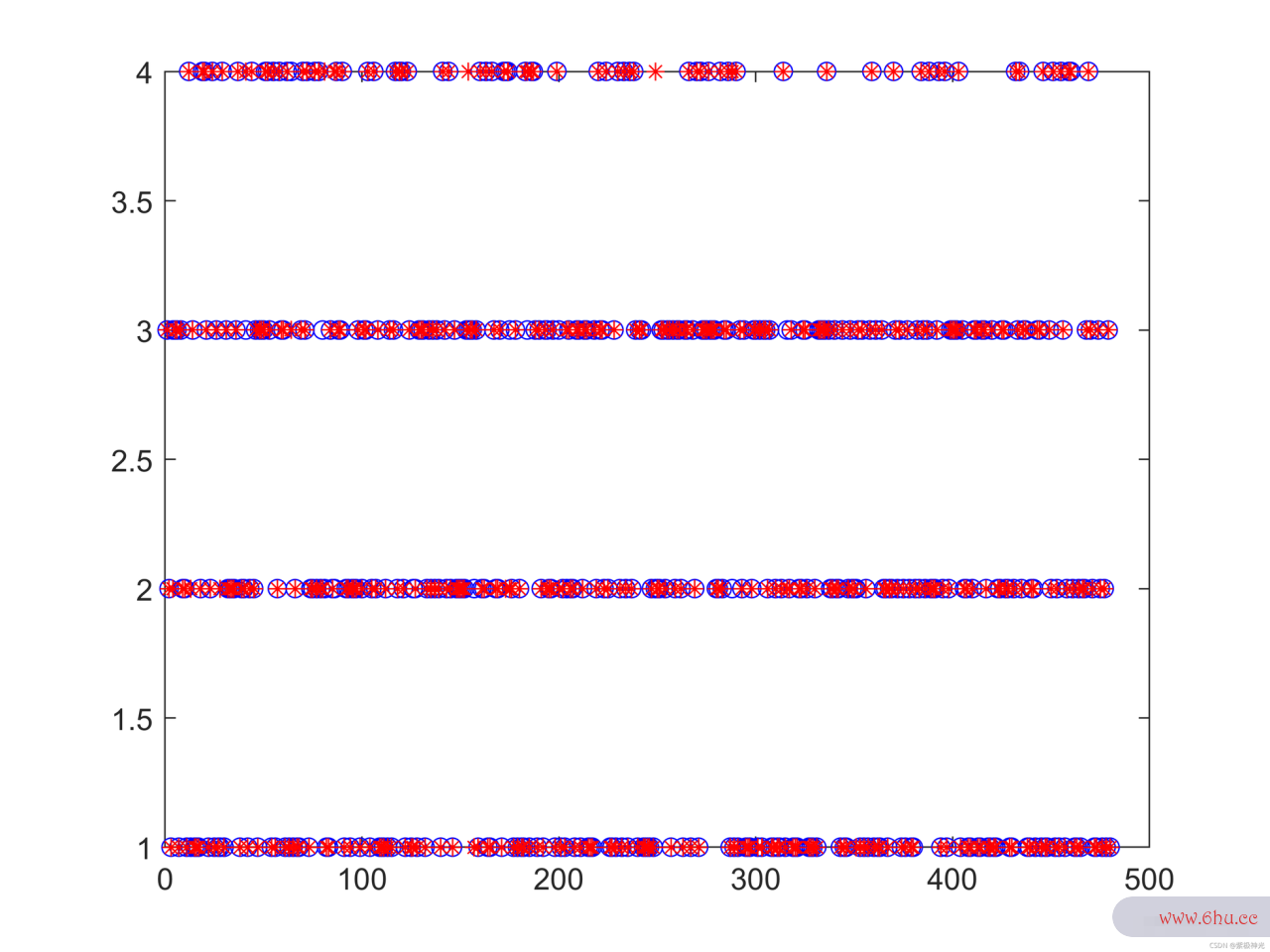
三、运行结果
四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本 2014a
2 参考文献神经网络是什么 [1] 包子阳,余继周,杨杉.智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例(第2版)[M].电子工业大学生创新创业大赛出版社,2016. [2]张岩,吴水根.MATLAB优化算法源代码[M].清华大学出版社,2017. [3]周品.MATLAB 神经网络设计与应用[M].清华大学出版社,2013. [4]陈明.MATLAB神经网络原理与实例精解[M].清华大学出版社,2013. [5]方清城.MATLAB R2016a神经网络设计与应用28个案例分析[M].清华索引失效的几种情况大学出版社,2018.

评论(0)