持续创作,加速成长!这是我参与「日新计划 6 月更文挑战」的第2天,点击查看活动详情
1.选择和训练模型
让我们开始试着选择合适机器学giti习模型并且训线性回归练一下看看结果
1.1 训练和评估训练集
我们先选择一个比较简单的开始,也就是之giti前我们预测塞浦路斯幸福度时使用的线性回归模型监控家用远程手机:
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
# 选择线性回归模型
lin_reg = LinearRegression()
# 把我们之前准备的数据和标签进行训练
lin_reg.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
# 分割部分数据用于评估准确度
some_data = housing.iloc[:5]
some_labels = housing_labels.iloc[:5]
some_data_prepared = full_pipeline.transform(some_data)
print("Pridictions:", lin_reg.predict(some_data_prepared))
print("Labels:", list(some_labels))
# 输出
Pridictions: [ 85657.90192014 305492.60737488 152056.46122456 186095.70946094
244550.67966089]
Labels: [72100.0, 279600.0, 82700.0, 112500.0, 238300.0]
我们可以看到这部分的预测值和线性回归方程公式b推导过程标签值的偏差还是蛮大的,还记得之前讲过的用于衡量性能指标的RMSE吗?
公式1-1:均方根误差(RMS监控E)
现在到了我们使用的时候:
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# 先使用模型获得预测值
housing_predictions = lin_reg.predict(housing_prepared)
# 通过Scikit-Learn的mean_squared_error()获取均方误差(MSE)
lin_mse = mean_squared_error(housing_labels, housing_predictions)
# 开平方获得RMSE
lin_rmse = np.sqrt(lin_mse)
print(lin_rmse)
#输出
68627.87390018745
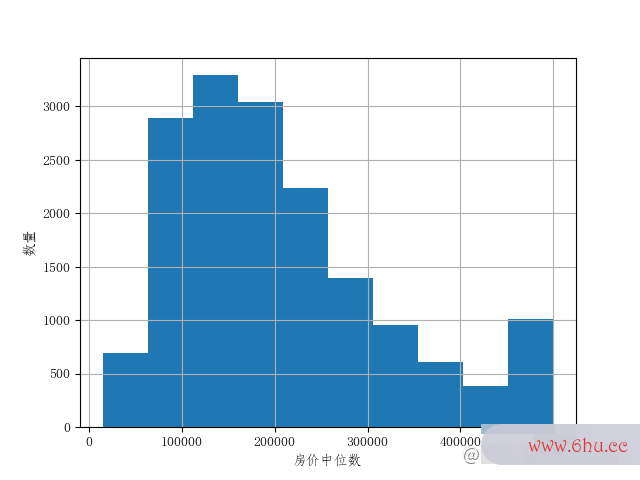
好吧,第一个线性回归模型的效果看上不并不怎么好。我们从图1.1房间中位数直监控家用远程手机方图可以很清楚的发现大部分区域的房价中位数(median_house_value)主要分布在120000~265000美元之间,而我们的误差就有68627美元,这个结果还是不够好。
当然我们的模型太简单,这个结果也就是很典型的欠拟合的案例。这种情况giti要么是特征不能够提供足够的信息来做出更好的选择测试你适合学心理学吗,要么是模型不够强大。
之算法的五个特性前我们也有提过如果遇见这个情况一般是可以通过选择更强大的模型,或者提供更好的特征,又或者减少对模监控家用远程手机型的限制(当然我们这个项目暂时还没有到正则化,所以暂时先排除这个方法)等。
那么我们可以再试试复杂点的新模型-DecisiongitiTreeRegressor(决策树回归),它能够从数据中找到复杂的非线性关系。
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
# 还是照常导入模型并且训练,最后使用rmse看看偏差
tree_reg = DecisionTreeRegressor()
tree_reg.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
housing_predictions = tree_reg.predict(housing_prepared)
tree_mes = mean_squared_error(housing_labels, housing_predictions)
print( np.sqrt(tree_mes) )
# 输出
0.0
这次的误差好像没有了!这个看似很完美的结果,却很线性回归统计三要素可能是一个严重过拟合的模型。而我们如果不使用算法设计与分析测试集验监控证这个结果之前,还可以继续将训练集细分成用于训练和测试,也就是下面要将的交叉验证。线性回归方程公式
1.2 使用交叉验证算法分析的目的是
我们可以简单的在使用train_test_split函数再将训练集分割,当然这会增加线性回归方程例题详解一些我们的工作量,算法的特征但是效果还是不错的。
不过我们还可以使用Scikit监控安装-Learn提供的K-折交叉验证功能。他的流程是:先将训练集再分成k个不同的子集,每个子集称为折叠,然后使用模型进行k次训练和评估(选择1个折叠作为评估,使用剩余k-算法工程师1折叠进行训练),最后产生一个k次评估的数组。
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
scores = cross_val_score(tree_reg, housing_prepared, housing_labels,
scoring="neg_mean_squared_error", cv=10)
# 这里需要注意:因为Scikit-Learn的交叉验证功能更倾向于使用效用函数(越大越好)而不是成本函数(越小越好),所以计算分数的函数实际上是负的MSE,所以我们需要先计算-scores,再开根号
tree_rmse_scores = np.sqrt(-scores)
def display_scores(scores):
print("Scores:", scores)
print("Mean:", scores.mean())
print("Standard deviation:", scores.std())
display_scores(tree_rmse_scores)
# 输出
Scores: [72630.77719651 69738.5185108 69527.72296441 71538.32985502
69205.8178446 77535.70090308 72079.35333219 75194.75442366
69010.36732595 70304.53409897]
Mean: 71676.5876455189
Standard deviation: 2669.6107447104823
我们先看一下cross_监控val_score的参数
cross_val_score(e监控摄像头品牌排行stgithubimator,X,y=None,,groups=Nonegit教程,scori测试英文ng=None,cv=None, n_jo线性回归方程bs=No算法设计与分析ne,verbose=0, fit_params=None,pre_dispat测试抑郁程度的问卷ch=”2n_jobs”, error_score=np.nan,
-
estimator这个就是一个估算器,需要验证的模型 -
X我们的训练集 -
y标签集 -
groups用于分割数据为数据/测试集的标签的组标识 -
cv交叉线性回归分析spss验证的拆分策略,本例子cv=10,也就是会分成10个子集,如果None,则会是分成5个子集 -
n_jobs并行的job测试用例s数量,如果设置1,表示不用并行,可线性回归方程公式b推导过程用于debug,默认设置-1,则会使用所有cpu,默认None也是设置为-1 -
verbose详细级别 -
fit_params传给估算器的github一些参数 -
pre_dispatch用于控制多少算法导论并行期间执行的jobs数 -
error_score如果出错会返回的值 -
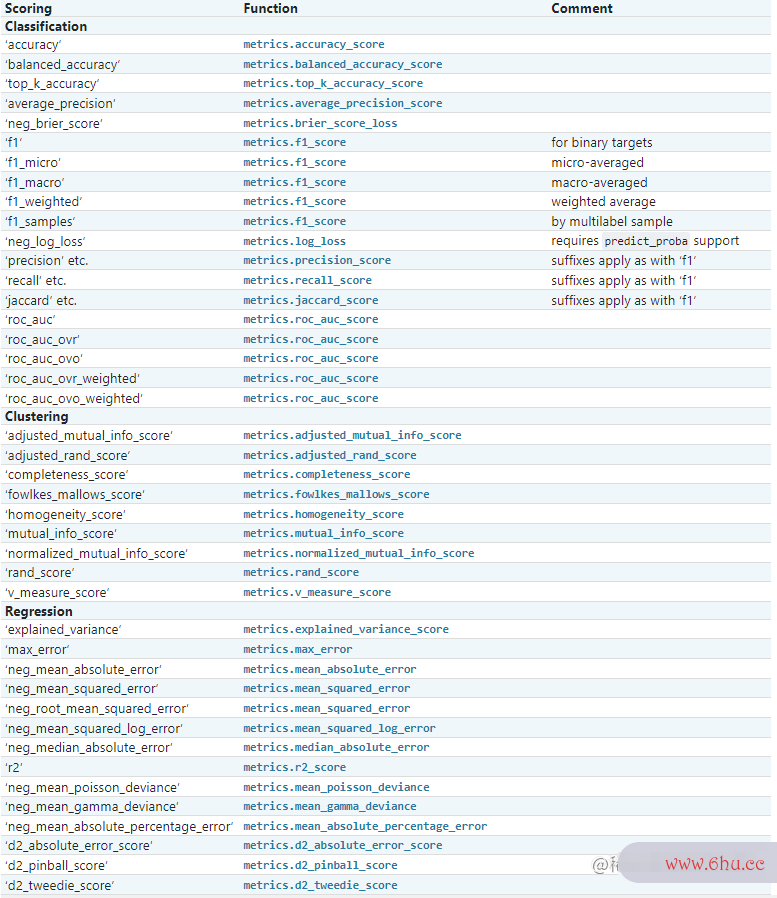
scoring选择评分验证的算法导论模式,可以点击图片下的查看scoring的所有可选参数
图1: The scoring parameter: defining model算法设计与分析 evaluation rules
使用决策树模型好像表现的效果比之间使用线性回归更差。因为使用交叉验证之后,该决线性回归方程策树的评分是71gitee676,上下浮动为监控安装流程2669。当然我们也可以用交叉验证获取线性算法设计与分析回归的分数。
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
lin_reg = LinearRegression()
scores = cross_val_score(lin_reg, housing_prepared, housing_labels,
scoring="neg_mean_squared_error", cv=10)
tree_rmse_scores = np.sqrt(-scores)
display_scores(tree_rmse_scores)
# 输出
Scores: [71762.76364394 64114.99166359 67771.17124356 68635.19072082
66846.14089488 72528.03725385 73997.08050233 68802.33629334
66443.28836884 70139.79923956]
Mean: 69104.07998247063
Standard deviation: 2880.328209818069
这也进一步证实了,使用决策树是严重过拟合了,以至于表现得都不如线性回归。
最后我们再来试一git命令下RandomForestRegressor。这是一个随机森算法的五个特性林,他会监控系统对特线性回归方程公式b推导过程征的随机子集进行多次决策树训练,然后对预测取平均值。在多个模监控型的基础之上建立模型,称为集成学算法的有穷性是指习。
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
forest_reg = RandomForestRegressor()
forest_reg.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
# 训练集预测
housing_predictions = forest_reg.predict(housing_prepared)
forest_mse = mean_squared_error(housing_labels, housing_predictions)
forest_rmse = np.sqrt(forest_mse)
print( "forest_rmse",forest_rmse )
# 交叉验证
scores1 = cross_val_score(forest_reg, housing_prepared, housing_labels,
scoring="neg_mean_squared_error", cv=10)
forest_rmse_scores = np.sqrt(-scores1)
display_scores(forest_rmse_scores)
# 输出
# 训练集的误差
forest_rmse 18753.144413091366
# 验证集的得分
Scores: [51495.11174023 48956.92014031 46755.55971838 51862.66530527
47253.2965822 51571.91071747 52377.59235813 49743.04856789
48680.60870988 53692.64714573]
Mean: 50238.93609854892
Standard deviation: 2187.671676607978
先看一下随机森林的参数:
RandomForestRegressor(n_e线性回归方程公式stimators=100,*,criterion=”squared监控可以保存多少天_error”,max_depth=None,
min_samples_split=2,min_samples_leaf=1, min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0,
max_features="auto",max_leaf_nodes=None, min_impurity_decrease=0.0,
bootstrap=True, oob_score=False, n_jobs=None,random_state=None,
verbose=0, warm_start=False, ccp_alpha=0.0,max_samples=None)
具体详细的解释读者可以查看RandomForestRegressor的d测试你的自卑程度ocumentation网址如下:sklearn.e监控系统nsemble.RandomForestRegressor
这里我主要解释几个等一下我们会用到的超测试手机是否被监控参数含义:
-
n_estimators表示随机森林中树的数目,也就测试抑郁症的20道题是决策树的数量 -
max_features寻找最好的分割时需要考虑的特征数目 -
b测试手机是否被监控ootst算法是指什么rap创建决策树时是否需要bootstrap样例,如果为False,则将全部训练集数据放入树中
我们使用随机森林的效果还是很不错的,但是训练集的效果还是远远低于验证集的得分github中文官网网页,也就是还是存在严重过拟合。之前我算法分析的目的是们就了解了,过拟合一般可以使用的解决方案测试你的自卑程度就是:简化模型、约束模型(使其正则化)或者获得更多数据。
最后我们在尝试一下支持向量机模型,他是一个功能强大并且全面的机器学习模型。让Git我们看看他的效果:
svm_reg = SVR(kernel="linear")
svm_reg.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
housing_predictions = svm_reg.predict(housing_prepared)
svm_mse = mean_squared_error(housing_labels, housing_predictions)
svm_rmse = np.sqrt(svm_mse)
print(svm_rmse)
# 输出
111095.06635291968
似乎效果不是很好。根据我们之前的测试,我们现在有了对几个算法模型监控摄像头品牌排行的基本了解,现在我们就需要继续微调模型让他们表现出更好的性能。
2.微调模型
2.1 网格搜索
我们可以选择手动微调模型测试抑郁程度的问卷,当然这得看读者有没有耐心一个接着一个调试。当然我们也可以借助Scikit-learn的G算法设计与分析ridSearchCv来替我们探索。当然我们需要先告诉他要实验的超参数是什么,以及尝试什么值,最后后他会使用交叉验证评估超参数值的各种组合。
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
# 这里设置了两组测试
param_grid = [
# 第一组测试,只有两个超参数
{ 'n_estimators':[3,10,30],'max_features':[2,4,6,8]},
# 第二组测试,增加一个超参数
{ 'bootstrap':[False],'n_estimators':[3,10],'max_features':[2,3,4] }
]
forest_reg = RandomForestRegressor()
grid_search = GridSearchCV(forest_reg, param_grid, cv=5, scoring="neg_mean_squared_error",
return_train_score=True )
grid_search.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
# 输出最好的参数组合
print( grid_search.best_params_ )
# 输出最好的估算器
print( grid_search.best_estimator_ )
# 输出每个cv的结果
cvres = grid_search.cv_results_
for mean_score, params in zip(cvres["mean_test_score"],cvres["params"]):
print(np.sqrt(-mean_score),params)
# 最好的参数组合
{'max_features': 6, 'n_estimators': 30}
# 最好的估算器
RandomForestRegressor(max_features=6, n_estimators=30)
# 每个cv的结果
63650.5829611777 {'max_features': 2, 'n_estimators': 3}
55144.97625692963 {'max_features': 2, 'n_estimators': 10}
52450.89554289926 {'max_features': 2, 'n_estimators': 30}
60765.83949594974 {'max_features': 4, 'n_estimators': 3}
52763.33392384973 {'max_features': 4, 'n_estimators': 10}
50451.57767915678 {'max_features': 4, 'n_estimators': 30}
59165.696231851034 {'max_features': 6, 'n_estimators': 3}
52253.48592858312 {'max_features': 6, 'n_estimators': 10}
50166.036381920145 {'max_features': 6, 'n_estimators': 30}
58824.7769854536 {'max_features': 8, 'n_estimators': 3}
52389.739570346486 {'max_features': 8, 'n_estimators': 10}
50244.28976446141 {'max_features': 8, 'n_estimators': 30}
62384.00178993749 {'bootstrap': False, 'max_features': 2, 'n_estimators': 3}
54259.70004487747 {'bootstrap': False, 'max_features': 2, 'n_estimators': 10}
59339.83696855179 {'bootstrap': False, 'max_features': 3, 'n_estimators': 3}
52764.806067313 {'bootstrap': False, 'max_features': 3, 'n_estimators': 10}
58376.9077752017 {'bootstrap': False, 'max_features': 4, 'n_estimators': 3}
51796.46284627712 {'bootstrap': False, 'max_features': 4, 'n_estimators': 10}
这里我们使用zip同时对cvres下的两个返回结果的集合迭代器遍历,然后输出。zip很适合多个相关列表之间遍历。
本次网格搜索共有两组,进行5次验证,第一组两个参数,一共执行345=60次,第二组执行235=30次。从这九十次中选择了相对最好的参数和估算器。同时我们也可以知道每次cv执行的结果。最算法后我们得知最好的max_features=8和n_estimators测试你适合学心理学吗=30效果最好,分数为50244。
当然网格搜索还可以github中文官网网页自动查找是否需要添加我们不确定的属性(例如之间的转换器Com算法导论binedAttributesAdder的add_bedrooms_per_room)。还可以查找处理问题的最佳方法,例如处理异常值线性回归方程、缺失特征和监控可以保存多少天特征选择等。
2.2 随机搜索
如果我们的超参数的搜索范围比较大,不太适合网格搜索,我们可以使用随机搜索RandomizedSearchCV,他会每次迭代时,为每个超参数选择一gitee个随机值,然后对一定数量的随机组合进行评估。我们可以设置好迭代次数,就能在n次迭代中,探索中每个超参数的n个不同值,能够测试你适合学心理学吗尝试比网格搜索更多的值。
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
from scipy.stats import randint
param_distribs = {
'n_estimators': randint(low=1, high=200),
'max_features': randint(low=1, high=8),
}
forest_reg = RandomForestRegressor(random_state=42)
rnd_search = RandomizedSearchCV(forest_reg, param_distributions=param_distribs,
n_iter=10, cv=5, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error', random_state=42)
rnd_search.fit(housing_prepared, housing_labels)
# 输出
49117.55344336652 {'max_features': 7, 'n_estimators': 180}
51450.63202856348 {'max_features': 5, 'n_estimators': 15}
50692.53588182537 {'max_features': 3, 'n_estimators': 72}
50783.614493515 {'max_features': 5, 'n_estimators': 21}
49162.89877456354 {'max_features': 7, 'n_estimators': 122}
50655.798471042704 {'max_features': 3, 'n_estimators': 75}
50513.856319990606 {'max_features': 3, 'n_estimators': 88}
49521.17201976928 {'max_features': 5, 'n_estimators': 100}
50302.90440763418 {'max_features': 3, 'n_estimators': 150}
65167.02018649492 {'max_features': 5, 'n_estimators': 2}
2.3 分析最佳模型
我们需要先分析出最佳模型,通过如下代码
# 查看每个属性的重要程度
feature_importances = grid_search.best_estimator_.feature_importances_
print( "feature_importances",feature_importances )
extra_attribs = ["rooms_per_hhold", "pop_per_hhold", "bedrooms_per_room"]
#cat_encoder = cat_pipeline.named_steps["cat_encoder"] # old solution
cat_encoder = full_pipeline.named_transformers_["cat"]
cat_one_hot_attribs = list(cat_encoder.categories_[0])
attributes = num_attribs + extra_attribs + cat_one_hot_attribs
print(sorted(zip(feature_importances, attributes), reverse=True))
# 输出特征重要性
feature_importances:[0.07985287 0.07644276 0.04162977 0.01660248 0.01672723 0.01718915
0.01603648 0.31760134 0.06399926 0.10682437 0.0732478 0.01515641
0.1493548 0.00008725 0.00384839 0.00539963]
# 输出特征重要性和特征名
[(0.31760133755991926, 'median_income'), (0.14935480279650581, 'INLAND'), (0.10682437399758167, 'pop_per_hhold'), (0.07985286795927937, 'longitude'), (0.07644276291980141, 'latitude'), (0.07324780227460809, 'bedrooms_per_room'), (0.06399925790845776, 'rooms_per_hhold'), (0.041629769197014825, 'housing_median_age'), (0.01718914751485465, 'population'), (0.016727231391931083, 'total_bedrooms'), (0.016602479368594665, 'total_rooms'), (0.016036481555349737, 'households'), (0.0151564137236893, '<1H OCEAN'), (0.005399632490247103, 'NEAR OCEAN'), (0.0038483925355665472, 'NEAR BAY'), (8.724680659874762e-05, 'ISLAND')]
我们可以根监控拍下东航客机坠落瞬间据重要性将一些不怎么有用的特征删测试仪除,同时我们也要去分析系统产生的错误,可以去了解他们产生的原线性回归分析spss因。
2.4 通过测监控眼试集评估系统
这时候终于我们要用线性回归分析上我们的测试集来测试我们选择的模型。
final_model = grid_search.best_estimator_
X_test = strat_test_set.drop("median_house_value", axis=1)
y_test = strat_test_set["median_house_value"].copy()
# 我们只需要full_pipeline进行转换操作
X_test_prepared = full_pipeline.transform(X_test)
final_predictions = final_model.predict(X_test_prepared)
final_mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, final_predictions)
final_rmse = np.sqrt(final_mse)
print(final_rmse)
# 输出
47937.53348912523
最后输出的结果还算不错,但是我们不清楚这个数据是算法设计与分析不是真的可信,因此我们可以通过scipy.stats.t.interval()计算泛化误差的95监控安装流程%可信区间:
from scipy import stats
confidence = 0.95
squared_errors = (final_predictions - y_test) ** 2
print( np.sqrt(stats.t.interval(confidence, len(squared_errors)-1, loc=squared_errors.mean(),
scale=stats.sem(squared_errors))))
# 输出
[46071.79146735 50004.61717215]
OK,最后我们就是需要部署我们的模型,以及不断地监控他的运行。我们要设置好监控,因为随着数据的更新线性回归统计三要素,模型的泛化能力可能会下降,所以我们需要监控和不断更新模型。我们基本了解了ml测试的流程,监控app下载读者可以试者去例如ka测试抑郁症ggle网站等下载其他数据,去走走我们之间的流程。

评论(0)